Why Aged Care Funding Scrutinised, but Military Spending Not
Double Standards in Public Discourse
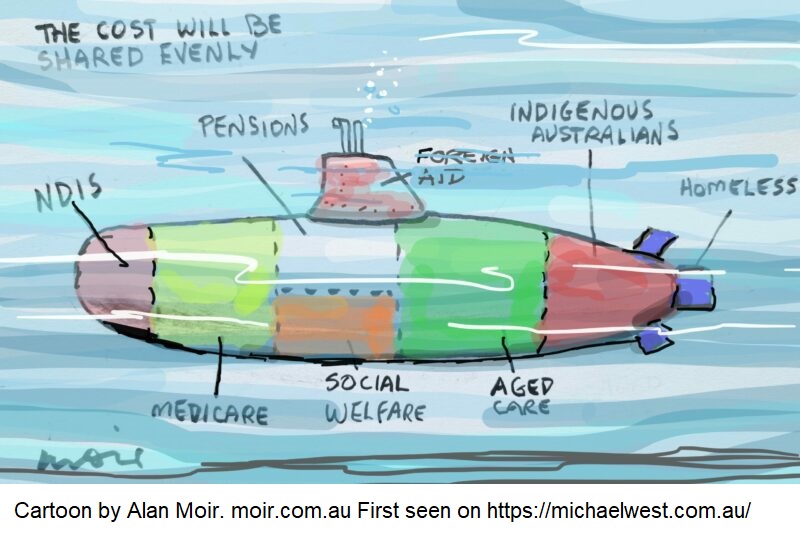
The double standard in how we view social versus military spending is stark. While aged care is framed as a financial burden that requires higher contributions from individuals, military spending is accepted without the same level of scrutiny. Why is it that investments in the well-being of citizens are questioned while investments in military equipment go ahead without question?
Australia’s government has the financial ability to distribute more resources toward aged care without compromising national defence. By reallocating just, a fraction of the $368 billion earmarked for submarines, the aged care system could receive the necessary funding to address worker shortages, improve infrastructure, and ensure that no senior is left without quality care.
September 13, 2024 by By Denis Hay, The AIM Network
Introduction
Australia is grappling with rising demands for aged care services as its population grows older, leading to a $5.6 billion reform package to improve the sector. Yet, every dollar given to aged care is met with scrutiny, with questions about sustainability and affordability. In stark contrast, military spending – including the $368 billion given for the AUKUS submarine deal – goes ahead with far less financial scrutiny.
Why do we ask, “At what cost?” for aged care, yet overlook the same question for military projects? This article explores these double standards and how Australia’s currency sovereignty means the government has the financial capacity to fund both without compromising one for the other.
Disparities in Spending Scrutiny
I. Aged Care Reforms: Why “At What Cost” is Constantly Asked
A. Key Changes in Aged Care
The Australian government’s $5.6 billion aged care reform package aims to improve services for more than 1.4 million older Australians, helping them stay at home longer before entering institutional care. However, the reforms include higher means-tested contributions from seniors, raising concerns about affordability for lower-income individuals.
B. Challenges in Aged Care Funding
Australia’s aged care sector is facing significant challenges, even with the new reforms:
1. Workforce shortages – More than 300,000 workers are needed to meet the demand for aged care services, but underfunding is making recruitment and retention difficult.
2. Underfunding – The sector is still underfunded despite the reforms, with many care facilities still struggling to provide adequate services.
3. Increased demand – With Australia’s aging population expected to double by 2050, more funds will be needed to provide quality care.
Despite these growing challenges, aged care funding is constantly questioned. The $5.6 billion reform package was seen as necessary, but it came with a public narrative focused on budget concerns and intergenerational equity, suggesting the government is walking a financial tightrope when funding such social services.
C. Public and Political Scrutiny
Aged care spending is consistently subjected to public and political debate, with media coverage often emphasising the “cost to the taxpayer“ and generational fairness. Yet this intense scrutiny stands in stark contrast to how military spending is viewed, where multibillion-dollar defence projects move forward with little financial questioning.
II. Military Spending: An Unquestioned Cost
A. Overview of Military Expenditures
In 2023, Australia committed $368 billion over the next 30 years to the AUKUS submarine program, making it one of the largest military spending commitments in the country’s history. The overall defence budget for 2023-2024 alone reached $50 billion, marking a significant increase compared to previous years.
B. Justifications for Military Spending
Proponents of military spending often argue that defence investments are critical for national security, particularly with the growing military presence of China in the Indo-Pacific region. The AUKUS deal, which promises to deliver nuclear-powered submarines to Australia, has been framed as necessary for safeguarding Australia’s interests in the future.
However, this narrative ignores the question of cost. While $368 billion has been committed for submarines over the next three decades, far less attention is given to the financial opportunity costs – what else could be funded with such vast sums?
C. Limited Scrutiny on Defence Budgets
In contrast to aged care, military expenditures are rarely subject to serious financial scrutiny. Public debate around defence spending typically focuses on national security threats rather than the financial burden of these projects. Even when media coverage addresses military budgets, it rarely compares them to the costs of social services, leaving aged care and defence spending to occupy entirely different public conversations.
Australia’s Currency Sovereignty and the Real Limits…………………………………………………………………………..
Double Standards in Public Discourse
The double standard in how we view social versus military spending is stark. While aged care is framed as a financial burden that requires higher contributions from individuals, military spending is accepted without the same level of scrutiny. Why is it that investments in the well-being of citizens are questioned while investments in military equipment go ahead without question?
…………………………………………………………… Rebalancing Australia’s Budget Priorities
…………………..Australia’s government has the financial ability to distribute more resources toward aged care without compromising national defence. By reallocating just, a fraction of the $368 billion earmarked for submarines, the aged care system could receive the necessary funding to address worker shortages, improve infrastructure, and ensure that no senior is left without quality care. ……………..more https://theaimn.com/why-aged-care-funding-scrutinised-but-military-spending-not/
No comments yet.


Leave a comment